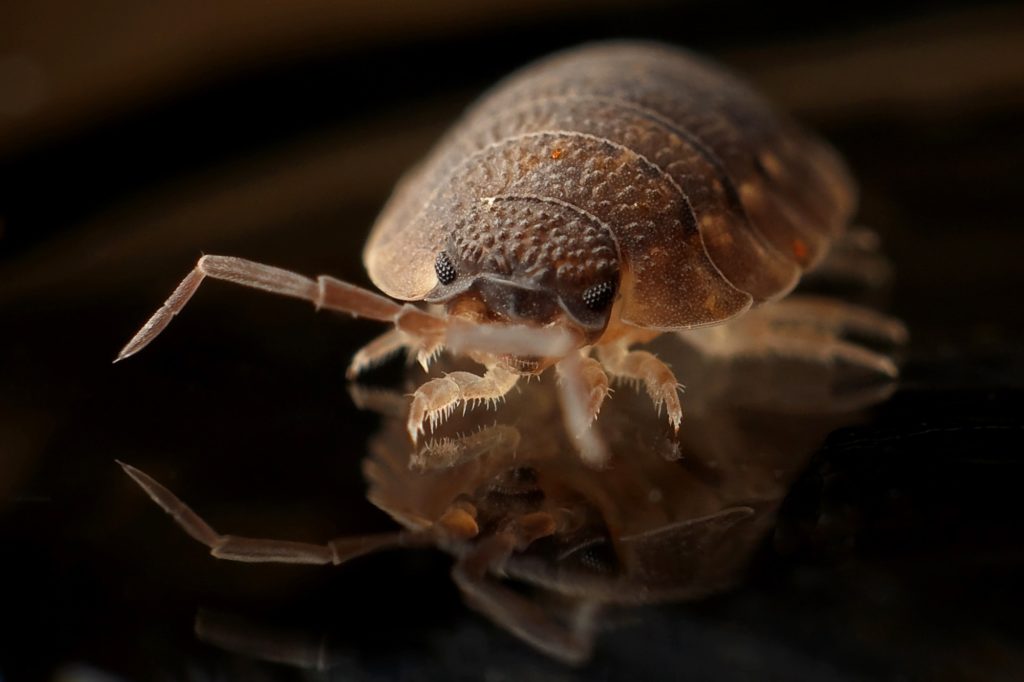
Bed bugs are a type of insect that feed on human blood, usually at night.[7] Their bites can result in a number of health effects including skin rashes, psychological effects and allergic symptoms.[5] Bed bug bites may lead to skin changes ranging from invisible to prominent blisters.[1] Symptoms may take between minutes to days to appear.[2] Itchiness is common, while some may feel tired or have a fever.[2] Typically, uncovered areas of the body are affected and three bites occur in a row.[2] Bed bugs bites are not known to transmit any infectious disease.[5][7]
Bed bug bites are caused primarily by two species of the insect Cimex: Cimex lectularius (the common bed bug) and Cimex hemipterus.[3] Their size ranges between 1 and 7 mm.[7] They spread by crawling between nearby locations or by being carried within personal items.[2] Infestation is rarely due to a lack of hygiene but is more common in high-density areas.[8][2] Diagnosis involves both finding the bugs and the occurrence of compatible symptoms.[5] Bed bugs spend much of their time in dark, hidden locations like mattress seams or cracks in the wall.